PI Name & Affiliation:
Dr. Annamalai Senthil Kumar
Professor, Director CO2
CO2 Research and Green Technologies Centre
Funding Agency: Royal Academy of Engineering, UK
Scheme: Royal society of chemistry (RSC)
Overlay: Rs. 3,58,303
Duration of the Project: 1 Years

Dr. Annamalai Senthil Kumar
Graphical Abstract
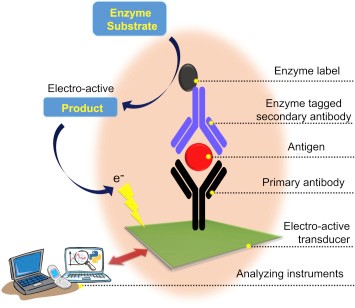
Project Description
The typhoid disease caused by Salmonella typhi is a major health problem in developing countries. In general, this disease is diagnosed either by culture isolation from clinical specimens or by the detection of the antibodies in the patient’s serum. Since the cultural isolation and further characterization of biochemical tests take a very long time, blood-serum antibody-based detection was referred widely for S. Typhi diagnosis. Several reports appeared for detection of these antibodies by using various methods such as Widal-agglutination, bentonite-flocculation, antiglobulin-hemagglutination, indirect-hemagglutination, latex-agglutination, counter-immune-electrophoresis and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) etc. Indeed, electrochemical immunosensor was rarely reported for this purpose (Handbook of Immunoassy Tech., 2018). A Scopus index ® literature search on keywords, electrochemical immunosensor & typhoid, there is only one report available. This report belongs to a preliminary amperometric immunosensing of Typhoid-antibody (Ab1-Ty) using a screen-printed electrode that has been modified with recombinant flagellin fusion protein and enzyme alkaline phosphatase-linked secondary antibody system.